Nápady 194+ Carbon Atom Parts Čerstvé
Nápady 194+ Carbon Atom Parts Čerstvé. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon?
Prezentováno Carbon Wikipedia
The other three are primary ( … 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it.For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary;
It is bonded to three carbon atoms. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); The other three are primary ( … It is bonded to three carbon atoms. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to.

The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°);. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°... The other three are primary ( …

18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. The other three are primary ( … It is bonded to three carbon atoms. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon?

For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary;.. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it.

It is bonded to three carbon atoms. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); The other three are primary ( … In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it... Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to.

18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? The other three are primary ( … A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); It is bonded to three carbon atoms.. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon?

18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. The other three are primary ( … It is bonded to three carbon atoms. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; The other three are primary ( …

Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to.. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to... The other three are primary ( …

Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. The other three are primary ( … In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to... 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it.

In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? The other three are primary ( …. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it.

For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary;.. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. The other three are primary ( … Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary;

For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary;. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. The other three are primary ( …. It is bonded to three carbon atoms.

The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); The other three are primary ( … 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon?

It is bonded to three carbon atoms... A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary;

The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.. The other three are primary ( …

18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon?.. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? The other three are primary ( …. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it.

07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it.

In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.

07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it.. . Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to.

A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it.

07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it... The other three are primary ( … In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.

In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it... 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it.

It is bonded to three carbon atoms. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. The other three are primary ( … The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon?

For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? It is bonded to three carbon atoms. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); The other three are primary ( … In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to... In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it.
/GettyImages-867635768-4daf6e4eef18405e9e0e77347a804094.jpg)
The other three are primary ( … In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it... Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to.

The other three are primary ( … The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it.

In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. The other three are primary ( … In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon?.. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.

The other three are primary ( … Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. The other three are primary ( … The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°);

The other three are primary ( … 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it... It is bonded to three carbon atoms.

A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. The other three are primary ( … 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°);. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary;

Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); The other three are primary ( … For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? It is bonded to three carbon atoms.. It is bonded to three carbon atoms.
/GettyImages-867635768-4daf6e4eef18405e9e0e77347a804094.jpg)
For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; The other three are primary ( … The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it.. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.

07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. The other three are primary ( …. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon?

The other three are primary ( ….. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.. The other three are primary ( …

07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary;.. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to.

For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); It is bonded to three carbon atoms. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. The other three are primary ( … Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary;. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.

A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. The other three are primary ( … It is bonded to three carbon atoms. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary;. The other three are primary ( …

18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon?.. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°... A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.

It is bonded to three carbon atoms.. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; The other three are primary ( … It is bonded to three carbon atoms. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? It is bonded to three carbon atoms.

In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°);.. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon?

The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°);. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; The other three are primary ( … 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it.

18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon?.. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to... It is bonded to three carbon atoms.
It is bonded to three carbon atoms.. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. The other three are primary ( … For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. It is bonded to three carbon atoms... A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.

Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. The other three are primary ( …. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it.

07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it.

Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to.. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.

For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary;. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. The other three are primary ( … The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? It is bonded to three carbon atoms. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; The other three are primary ( …

For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary;. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. The other three are primary ( … For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°);.. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.
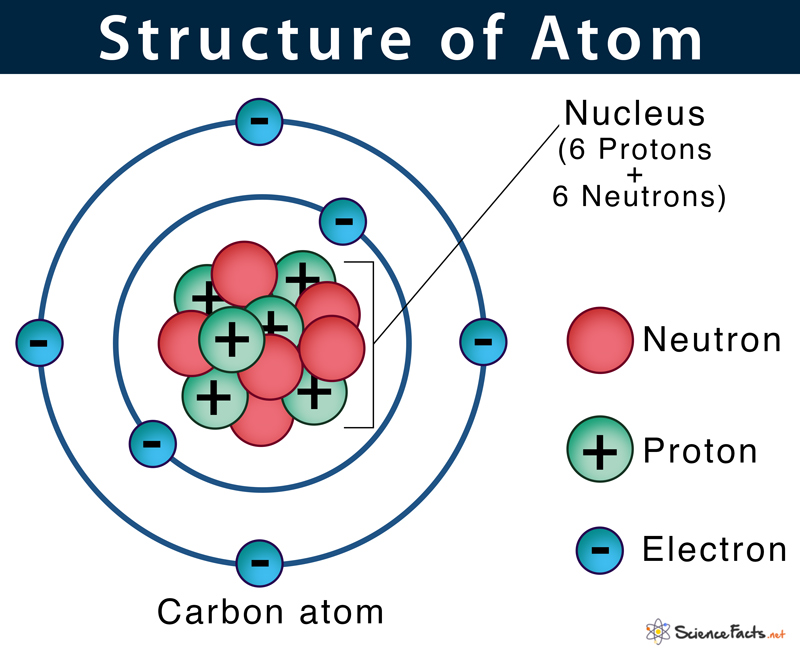
07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it... .. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon?

A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.. . A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.

07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it... A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it.. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°);

In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it.. . A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°.

In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it.. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to.. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°);

A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. A carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms is tertiary, and is designated by 3°. Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. It is bonded to three carbon atoms. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it.

In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it... The other three are primary ( … Carbon can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary depending on the number of carbon atoms it is bonded to. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); It is bonded to three carbon atoms.

In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. 18/03/2008 · 18/03/2008 · what are parts of an atom of carbon? The other three are primary ( … The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°); For example, when we examine the structure of isobutane, we see that one of the four carbon atoms is tertiary; In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. 07/04/2017 · a carbon atom in an organic compound is labeled or classified based on the number of bonds and type of atoms attached to it. The internal carbon atom is tertiary (3°);

In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it.. . In this post, we will specifically focus on the classification of carbon based on the number of other carbon atoms attached to it.
